Terrestrial Ecology
-

Biogeochemical Hot Moments
Researchers install in situ, permeable solid phase-groundwater reaction cells into wells at DOE’s Rifle, Colorado, field site to investigate molecular-scale mechanisms governing uranium mobility in response to seasonally changing groundwater conditions. This work is supported by the Subsurface Biogeochemical Research activity in the Environmental System Science research area.
-

SPRUCE Enclosures
Spruce and Peatland Responses Under Changing Environments (SPRUCE) Project. Experimental enclosures provide warming from the tree tops to the deep soil for the Terrestrial Ecosystem Science-supported SPRUCE project. SPRUCE is an ecosystem-scale manipulation study to assess the response of northern peatland ecosystems to increases in temperature and exposures to elevated atmospheric carbon dioxide concentrations.
-

Field with Flowers
Collaborative Modeling Research. Scientists supported by the Multisector Dynamics activity in the EESM research area are discovering the potential implications of Earth system changes on land use, bioenergy production, and agricultural yields.
-

East River Catchment
Meandering stream in East River Catchment, Gunnison County, Colorado. One hypothesis is that hyporheic zone flow through organic carbon–rich sediments between meanders may have a large impact on integrated carbon cycling in the river basin. This occurrence suggests the need to capture hydrological and biogeochemical gradients at the fine scale (<1 m) and then upscale these gradients to the larger kilometer scale length of the river. Clearly a computational challenge, this process will require a new terrestrial modeling software framework.
-

Plant Virtual Plot Model
Interactions in a Virtual Plot Model. A virtual plant model that includes assemblages of individual plants with
explicitly resolved interactions between each plant and its above- and belowground environments would help bridge the gap between the scale of an individual plant and that of a crop, hillslope, or watershed. -

Next-Generation Ecosystem Experiments Arctic
An NGEE-Arctic researcher takes measurements amid a swarm of mosquitoes.
-

AmeriFlux Tower in Washington
Researchers inspect an eddy covariance flux tower at the Billy Frank Jr. Nisqually National Wildlife Refuge.
-

Oak Ridge National Laboratory’s FACE Experiment
Aluminum towers in the middle of sweetgum trees along the Clinch River in Tennessee were part of the Oak Ridge National Laboratory FACE experimental setup designed to determine how forests and ecosystems react to elevated atmospheric CO2.
-
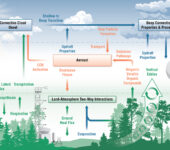
Mass and Energy Exchange from the Land Surface to the Atmosphere
The Atmospheric Radiation Measurement Mobile Facility deployment in Alabama’s Bankhead National Forest (AMF3-BNF) presents a unique opportunity to improve understanding and process-level model representation of coupled aerosol, cloud, and land surface processes (e.g., the crosscutting science drivers shown above) in an environment where such processes are strongly driven by local forcing.
-

Aerial View of SPRUCE
Aerial view of a Spruce and Peatland Responses Under Changing Environments (SPRUCE) site.