Human Genome Project
-

Chromosome 19
- Magenta and green. These regions reflect the unique patterns of light and dark bands seen on human chromosomes that have been stained to allow viewing through a light microscope.
- Red. The centromere, or constricted portion, of each chromosome.
- Yellow. Chromosomal regions that vary in staining intensity and are sometimes called heterochromatin (meaning “different color”).
- Yellow with thin magenta horizontal lines. Denote variable regions, called stalks, that connect a very small chromosome arm (a “satellite”) to the chromosome.
-
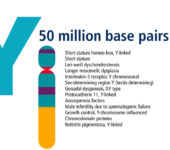
Chromosome Y
- Magenta and green. These regions reflect the unique patterns of light and dark bands seen on human chromosomes that have been stained to allow viewing through a light microscope.
- Red. The centromere, or constricted portion, of each chromosome.
- Yellow. Chromosomal regions that vary in staining intensity and are sometimes called heterochromatin (meaning “different color”).
- Yellow with thin magenta horizontal lines. Denote variable regions, called stalks, that connect a very small chromosome arm (a “satellite”) to the chromosome.
-

Chromosome X
- Magenta and green. These regions reflect the unique patterns of light and dark bands seen on human chromosomes that have been stained to allow viewing through a light microscope.
- Red. The centromere, or constricted portion, of each chromosome.
- Yellow. Chromosomal regions that vary in staining intensity and are sometimes called heterochromatin (meaning “different color”).
- Yellow with thin magenta horizontal lines. Denote variable regions, called stalks, that connect a very small chromosome arm (a “satellite”) to the chromosome.
-
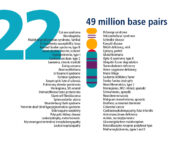
Chromosome 22
- Magenta and green. These regions reflect the unique patterns of light and dark bands seen on human chromosomes that have been stained to allow viewing through a light microscope.
- Red. The centromere, or constricted portion, of each chromosome.
- Yellow. Chromosomal regions that vary in staining intensity and are sometimes called heterochromatin (meaning “different color”).
- Yellow with thin magenta horizontal lines. Denote variable regions, called stalks, that connect a very small chromosome arm (a “satellite”) to the chromosome.
-
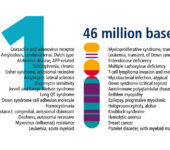
Chromosome 21
- Magenta and green. These regions reflect the unique patterns of light and dark bands seen on human chromosomes that have been stained to allow viewing through a light microscope.
- Red. The centromere, or constricted portion, of each chromosome.
- Yellow. Chromosomal regions that vary in staining intensity and are sometimes called heterochromatin (meaning “different color”).
- Yellow with thin magenta horizontal lines. Denote variable regions, called stalks, that connect a very small chromosome arm (a “satellite”) to the chromosome.
-

Chromosome 20
- Magenta and green. These regions reflect the unique patterns of light and dark bands seen on human chromosomes that have been stained to allow viewing through a light microscope.
- Red. The centromere, or constricted portion, of each chromosome.
- Yellow. Chromosomal regions that vary in staining intensity and are sometimes called heterochromatin (meaning “different color”).
- Yellow with thin magenta horizontal lines. Denote variable regions, called stalks, that connect a very small chromosome arm (a “satellite”) to the chromosome.
-

Chromosome 11
- Magenta and green. These regions reflect the unique patterns of light and dark bands seen on human chromosomes that have been stained to allow viewing through a light microscope.
- Red. The centromere, or constricted portion, of each chromosome.
- Yellow. Chromosomal regions that vary in staining intensity and are sometimes called heterochromatin (meaning “different color”).
- Yellow with thin magenta horizontal lines. Denote variable regions, called stalks, that connect a very small chromosome arm (a “satellite”) to the chromosome.
-

Chromosome 10
- Magenta and green. These regions reflect the unique patterns of light and dark bands seen on human chromosomes that have been stained to allow viewing through a light microscope.
- Red. The centromere, or constricted portion, of each chromosome.
- Yellow. Chromosomal regions that vary in staining intensity and are sometimes called heterochromatin (meaning “different color”).
- Yellow with thin magenta horizontal lines. Denote variable regions, called stalks, that connect a very small chromosome arm (a “satellite”) to the chromosome.
-

Chromosome 1
- Magenta and green. These regions reflect the unique patterns of light and dark bands seen on human chromosomes that have been stained to allow viewing through a light microscope.
- Red. The centromere, or constricted portion, of each chromosome.
- Yellow. Chromosomal regions that vary in staining intensity and are sometimes called heterochromatin (meaning “different color”).
- Yellow with thin magenta horizontal lines. Denote variable regions, called stalks, that connect a very small chromosome arm (a “satellite”) to the chromosome.